Wireless Private Network Solution for Chemical Industry Parks (Port Areas)
I. Analysis of Key Points for Wireless Network Construction in Chemical Industry Parks
- Environmental Complexity: Large storage tanks, pipe racks, production equipment, and various structures are distributed within chemical industry parks, creating a complex electromagnetic propagation environment. Wireless signals need to overcome attenuation caused by reflection and absorption from metal obstacles to achieve full-area coverage.
- Safety and Reliability: Chemical production involves flammable and explosive substances. Wireless communication equipment must meet explosion-proof requirements and operate stably in highly corrosive and wide-temperature-range environments. The communication system needs to have anti-interference capabilities and high reliability to ensure uninterrupted real-time transmission of production data.
- Service Diversity: Communication services in chemical industry parks are diverse, including video surveillance, equipment status monitoring, personnel positioning, environmental monitoring, and emergency command. Different services have different requirements for bandwidth, latency, and connection density, so the network needs to have differentiated service capabilities.
- Mobility Support: Scenarios such as park patrols and emergency response require seamless access for mobile terminals to ensure uninterrupted communication for personnel during movement.
- Network Security: As a key national infrastructure, the communication system of chemical industry parks needs to ensure network security based on the principle of “physical isolation” and protect the security of industrial data.

With the large-scale and complex development of chemical industry parks (port areas), traditional wired networks are increasingly insufficient in terms of coverage range, deployment flexibility, and emergency response. As a key infrastructure for the digital transformation of chemical industry areas, wireless private networks, leveraging their advantages of flexible deployment, wide coverage, and high bandwidth, are becoming a core technical means to improve the safety management level and operational efficiency of parks (port areas).
II. Comparison of Private Network Technologies and Products for Chemical Industry Parks
- Difficulties in Coordinating with Residents: Whether installing optical cables underground via trenching or overhead via pole erection, coordination with villages and residents along the route is necessary. Trenching for underground installation requires the construction of shafts for maintenance, while pole erection can only be completed after negotiating with farmers who own the land along the route. Nowadays, coordinating with villages and farmers has become increasingly difficult. In addition to the rising one-time construction costs, some farmers may even demand annual “rent”. Failure to pay such fees can lead to extreme situations, including damage to the optical cables.
- Vulnerability of Optical Cables to Damage: Overhead optical cables via pole erection cost slightly less than underground installation via trenching. However, overhead exposed cables are easily cut by passing vehicles, causing system network outages. Even when buried underground, optical cables may be damaged by village-level construction work such as trenching, resulting in short-term or even long-term network disruptions. Beyond accidental damage, optical and power cables are also prone to theft and cutting by criminals. Once damaged, repairs are more difficult and time-consuming.
- Impact of Optical Cable Splicing: Fewer splice points are better for optical fiber cabling, as splicing causes signal attenuation. In practice, however, intelligent on-site operations in chemical industry parks involve a large number of splice points—especially in locations frequently damaged. Repeated splicing can reduce signal strength below the sensitivity requirements of optical equipment; in the worst cases, entire optical cables may be rendered useless. Replacing these cables incurs significantly higher costs and can even cause system shutdowns.
- High Costs: The material cost of optical cables themselves is not high, but the costs of trench digging for underground installation or pole erection for overhead deployment have risen annually due to increases in labor costs and expenses for renting trenchers, cranes, and other equipment. Construction costs often reach tens of thousands of yuan per kilometer, driving up the overall system cost. Crossing roads with optical cables is even more troublesome: whether using “pipe jacking” for underground installation or overhead deployment, the costs are extremely high, and potential risks remain widespread.
- Long Construction Cycles: Trenching for underground optical cable installation or pole erection for overhead deployment is highly challenging. The longest phase of a project is often the construction period for optical cables, and the project duration is also positively correlated with construction costs.
Is a Wireless Communication System as Stable as an Optical Network? Is the Communication Link Reliable?
1. Wireless Public Network Technology – 4G/5G Technology
1) Access Limitations
2) Bandwidth Limitations
3) High Costs
4) Security Issues
2. Ordinary WiFi Wireless Networks
- Coverage: Most common WiFi systems are designed for indoor wireless coverage, with a typical coverage radius of less than 100 meters. To achieve full urban coverage, an excessive number of base stations would be required. Firstly, coordinating the construction of these base stations is difficult; secondly, managing and maintaining them is challenging. If relying on existing WiFi coverage systems of operators (which function as “public networks”), it would be hard to guarantee service quality, and network security would also be questionable.
- Services: Common WiFi systems are networks based on a sharing mechanism. They work well for data services such as web browsing without obvious issues. However, when used for video services that require stable bandwidth and large traffic—such as building a dedicated video surveillance network—WiFi systems fall short.
- Frequency: More critically, the current 2.4G frequency band is crowded with a large number of systems and devices competing for frequency resources. Major operators and numerous enterprises/institutions are building their own WiFi coverage systems, leading to severe mutual interference and a significant reduction in system availability.
3.Wireless WirelessProprietary Technology for Wireless Metropolitan Area Network —- iMAX 5G Wireless Metropolitan Area Network Communication System:
- Bandwidth Capacity: The maximum communication distance of various series of iMAX 5G broadband wireless products can reach 50 kilometers or even 100 kilometers in line-of-sight conditions, and the typical coverage radius of park base stations is 10 kilometers. The single-point communication bandwidth ranges from 100Mbps to 600Mbps, and it supports point-to-multipoint networking and N-sector capacity superposition networking, which can fully meet the bandwidth and coverage distance requirements of large-capacity, high-definition 1080P, and real-time transmission for the construction of chemical industry park monitoring systems.
- Performance Advantages: The system supports high-reliability technologies such as ring network and hot backup redundancy, and also supports technologies like routing, firewall, VPN, and VLAN, making it suitable for large-scale urban long-distance networking.
- Stability and Efficiency: The equipment inherits high-quality genes, with good operational stability and high reliability. It is a truly all-weather 7×24-hour uninterrupted operation device, with stable bandwidth and strong anti-interference ability.
- Safety and Reliability: It adopts access control, data encryption, and supports VLAN and VPN technologies to ensure the security of the transmission network at multiple levels and high standards. The equipment is of high quality and has good environmental adaptability, being a truly outdoor product.
- Good Economy: It requires a one-time investment, with no need for high link rental fees in the later stage. Under the same conditions, the investment in the iMAX 5G system is equivalent to the rental cost of optical cables for about 1-2 years. Moreover, it can be relocated at will, with convenient and quick installation, short construction period, and simple use, maintenance, and management.
- Flexible Deployment: The equipment is small in size and light in weight, taking only 1-2 working days to install, and is very easy to maintain and relocate.
- Communication Distance: Under visual conditions, the iMAX 5G dedicated communication system can achieve a maximum communication distance of more than 50 kilometers. Even the smallest integrated antenna system can easily meet the coverage requirement of a 10-kilometer radius.
- Transmission Bandwidth: The iMAX-8000H is a 300/600Mbps point-to-multipoint communication system, the iMAX-8000S is a 100Mbps point-to-multipoint communication system, and the iMAX-6000 is a point-to-point 150/300/600Mbps communication system.

III. Solution Design for Chemical Industry Park Private Networks
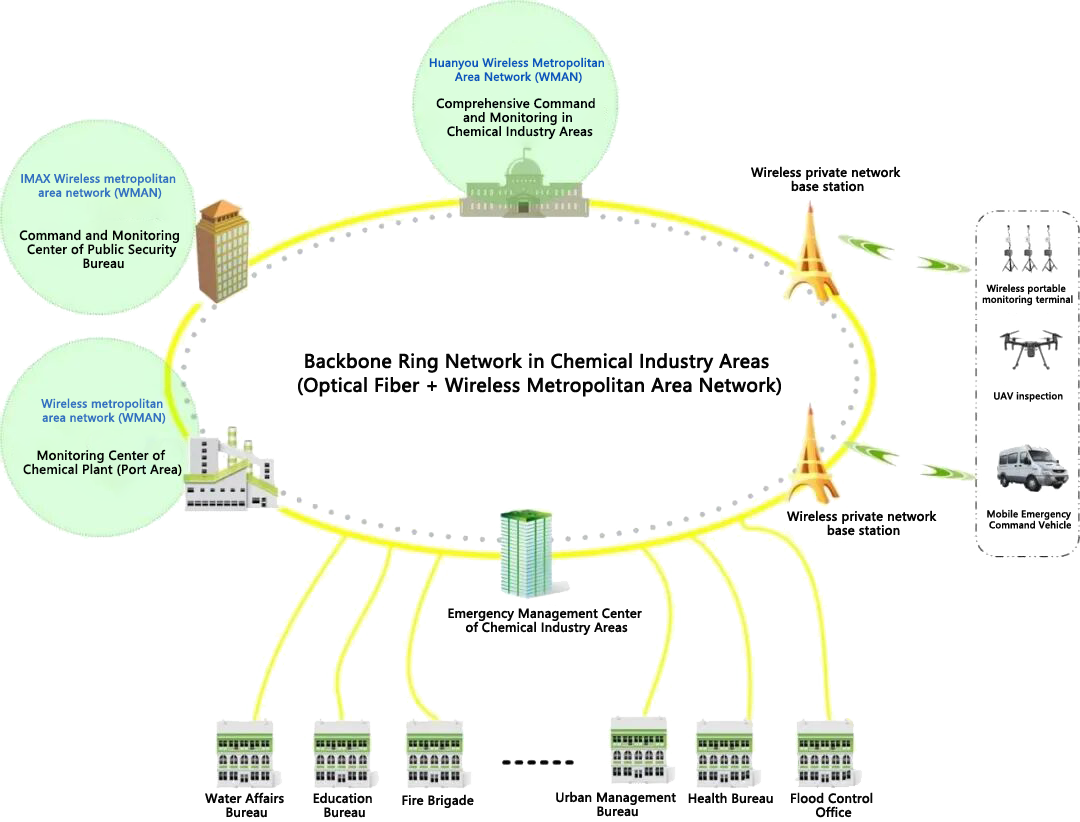
- Wireless MAN Backbone Transmission: Based on the iMAX 5G wireless MAN system or FibeAir IP microwave system, it provides wide-area coverage with a single base station covering a radius of 10-30 kilometers, and the maximum point-to-point transmission distance reaches 120 kilometers. The system supports high-speed data transmission of 300/600Mbps or even over 10G, meeting the needs of high-definition video surveillance and massive data collection in chemical parks.
- Flexible Coverage of Mesh Ad Hoc Network: The low-frequency Huanyou wireless Mesh system has the capability of self-organizing, self-healing mobile communication, and can achieve a transmission rate of 40M/80Mbps in non-line-of-sight environments, which is particularly suitable for emergency mobile communication coverage in complex device areas.
- 4G/5G Mobile Access: It supports the integrated networking of public and private networks, providing high-speed mobile access capabilities for mobile inspections, ensuring uninterrupted communication for personnel during movement, and is suitable for cloud access of mobile terminals such as mobile phones. Alternatively,
- WiFi High-density Access: Through OFDMA and MU-MIMO technologies, it significantly improves network throughput, reduces communication delay, and supports short-distance (within 100 meters) and large-bandwidth applications such as AR remote assistance and emergency expert command.
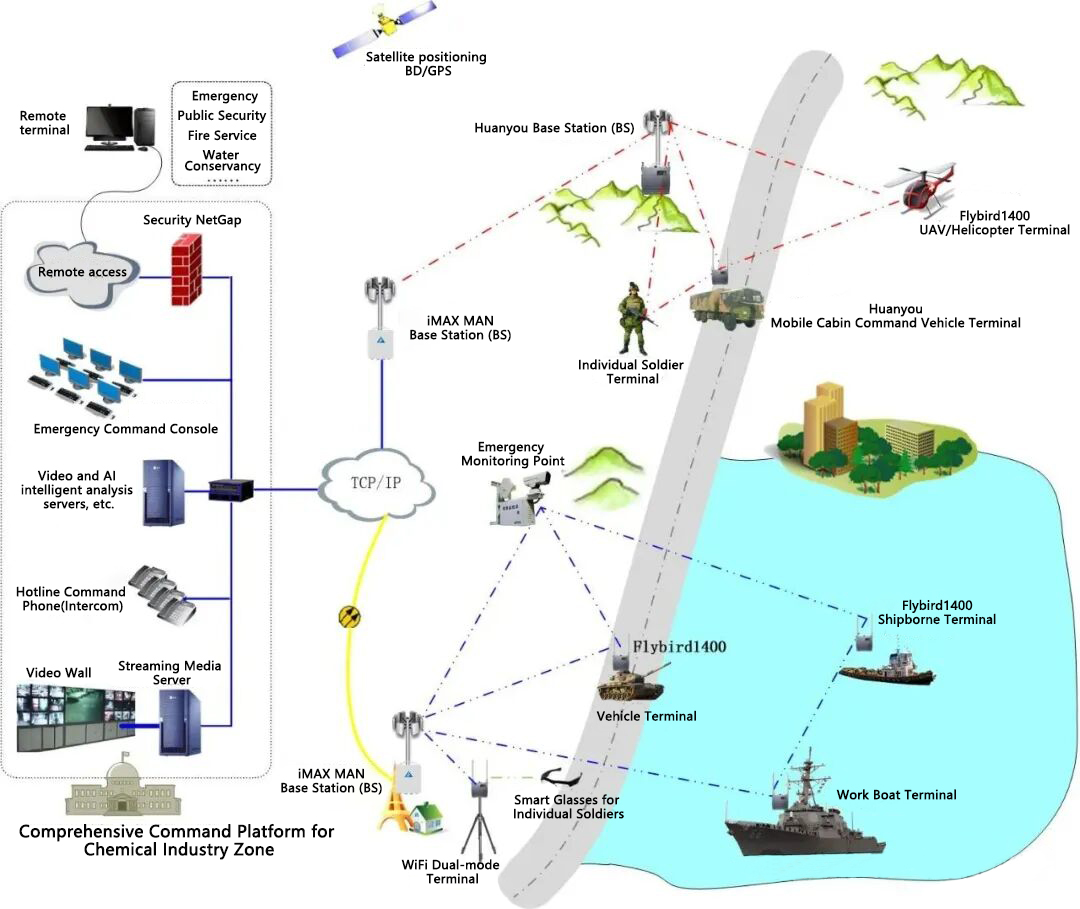

- Infrastructure investment savings: The wireless private network eliminates the need for large-scale wiring projects, saving more than 50% of infrastructure investment costs (or long-term data link rental costs). Construction coordination is easier, engineering difficulty is lower, and the construction cycle is shorter. Networking is often the most uncontrollable and time-consuming link in many IT and intelligent projects. The adoption of a wireless metropolitan area network (MAN) private network solution can significantly shorten the construction period of related projects, reducing costs and increasing efficiency for integrator partners.
- Rapid deployment reduces labor costs: Wireless devices are plug-and-play, with deployment speeds measured in days, often ten times or even a hundred times faster than wired networks. This greatly reduces the input of construction personnel and equipment, leading to a substantial decrease in labor costs.
- Flexible expansion saves upgrade expenses: Unlike traditional wired networks, upgrading the capacity of a wireless MAN does not require re-wiring. The addition of clients can be flexibly expanded, relocated, or moved according to user needs. Flexible expansion can be achieved by adding wireless systems, avoiding repeated investments.
- Improved production efficiency: Real-time data collection and mobile applications enhance inspection and personnel work efficiency by over 50%, reducing the input in manual inspections.
- Safety management benefits: Through real-time monitoring and early warning, safety accidents are effectively prevented, and potential losses from production interruptions are reduced.
- Decision support value: With the wireless MAN as the basic transmission channel, combined with digital twins, big data analysis, and AI-assisted decision-making systems, it can provide data support for production optimization, energy management, safety management, etc., facilitating the refined operation of chemical industrial parks.
- Device-level reliability: All wireless devices are designed with industrial-grade standards, meeting the IP67 protection rating, and operating within a temperature range of -40℃ to 75℃, which satisfies the requirements of harsh environments in chemical industrial parks. The mean time between failures (MTBF) of the devices exceeds 100,000 hours.
- Network-level reliability: The core backbone transmission links adopt 1+1 hot backup or ring network topology. Base stations support ring network protection or MESH self-healing, improving system reliability at the network structure level. Key nodes are networked using multi-link data mirroring (MLDM) technology or VRRP virtual hot backup redundancy technology. The network fault self-healing time is less than 50ms or even achieves zero-delay switching, ensuring uninterrupted services.
- Transmission encryption: Dynamic encryption algorithms are used to achieve end-to-end encryption, preventing data leakage and tampering.
- Network isolation: Logical isolation of different business systems is achieved through technologies such as VLAN, VPN, and Firewall.
- Intrusion detection: Real-time monitoring of network attack behaviors is performed, and protective measures are automatically activated, such as DoS attack protection.